How to Pass Level 9 Dividing in 10 Is Again
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q1: What is the relation between multiplication and sectionalization?
Ans:Multiplication and division are arithmetic operations which are inverse to each other. Multiplication is used to find out total number of objects within equal groups while sectionalization is used to identify number of objects in each equal grouping or number of equal groups. If 3 x half dozen = 18 and then eighteen ÷ three = vi or 18 ÷ 6 = 3.
Q2: How do you lot teach partition?
Ans:The beginning introduction to sectionalization will be sharing groups of objects into equal groups . Distributing something fairly into equal groups is called division. For example; dividing 12 items among four persons equally is a share of iii with each person which tin be mathematically expressed as 12 ÷ four = 3.
Q3: How do you write a sectionalisation sentence?
Ans:We write a division judgement using the equation: dividend ÷ divisor = caliber. When nosotros divide something equally into small groups, the complete group is called the dividend, number of items in each group is chosen quotient and the number of groups is called the divisor in a division sentence.
Overview of Sectionalisation
"Segmentation" in general terms is the derivative of word "separate". As the term refers to portioning of a number, it is a form of progressive or repeated subtraction. A given number is subtracted from another number till information technology becomes zero or less than the subtrahend.
A division equation looks like this:
9 % 3 = 3
Dividend Divisor Quotient
A division equation tin can besides be written equally a fractional number every bit follows:
nine / iii = 3 (Dividend / Divisor = Quotient)
"Partitioning" is one of the basic math skills introduced to kids in form three. At this level, kids are already familiar with addition, subtraction and multiplication. With the noesis of place value system and counting skills up to ten thousand, kids acquire the division by a unmarried digit and double-digit numbers in the pre-yard curriculum.
-
Math Games for Teaching Division
A step next to basics of addition, subtraction and multiplication (repeated add-on), division games instigate the key concept systematically for the kids. Partitioning Games on an interactive theme-equipped interface and based on real-life examples substantially boost the kids to learn.
- Learning & effect: The real challenge while learning mathematics is the application part. To nurture deep-rooted concepts with a clear agreement of the technique, immense do is required. With partition games, kids understand to equally distribute or split objects into smaller and equal groups. Gradually, the application part of "partitioning" for solving equations using word problems and logic puzzles helps the kids to overcome the math fright. Proficiency in the respective skill is the primal to excel in math in later grades while learning avant-garde math.
The projected learning outcomes are:
- Introduction to the concept of sectionalisation (short and long division)
- Understanding the process of division using different models; partition model and measurement model (using a number line)
- Framing mathematical equations with dissimilar signs used for division and relating to the associated math terms
- Dividing a number by another equally per the technique and representing the consequence in the terms, dividend, divisor, and residual
- Progressing to the segmentation of large numbers (upwards to 4-digit) with a 2-digit number
- Comprehending the noesis of the skill "segmentation" in the unlike fields of science, mathematics, and statistics
- Required math skills: As "partitioning" is a circuitous and central math skills; proficiency in basic math with the counting skills (up to 10,000), addition and subtraction (upward to four digit numbers) is required. Also, the understanding of multiplication tables and "know-how" technique to course the "multiplication tables", is highly useful for the short segmentation.
- Engagement: Comprehensive division games for kids up to grade-5 are instrumental in nurturing the basic math essential. The interactive theme-based interface engages the kids and motivates them to grasp the concept inside piece of cake steps. Schematically planned equally per the cadre math standards, math games are conducive to build confidence to excel in math.
Profusely illustrated practice worksheets adhering to the curriculum are best suited for homeschooling and serve as a versatile math homework help to kids.
-
Manipulatives used for teaching Division
- Counters: As kids are familiar with the use of counters for addition and subtraction using counters, learning the technique of multiplication becomes easy. As it'due south a class repeated add-on, using counters. "Division" using counters is the reverse procedure in which, instead of adding, "subtraction" is used. Division using counters is aforementioned as the partition model.
- The total number counters become "dividend".
- The number of groups in which counters are divided becomes the "divisor".
- To obtain the quotient, place an equal number of counters in each group.
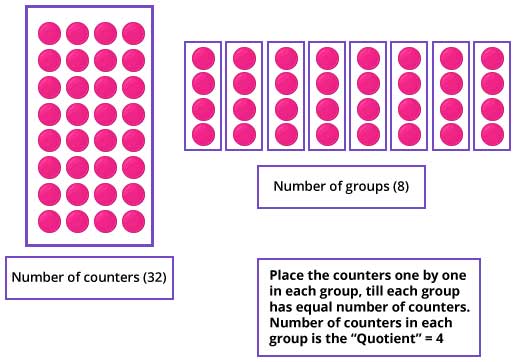
Reference image: Division using counters (without remainder), the division equation is 32 ÷ 8 = 4

Reference paradigm: Division using counters (with residue), the division equation is 34 ÷ eight = iv and the remainder is 2
- Base x blocks: The base 10 blocks are one of the most efficient ways to comprehend the decimal number organization. The smallest size block is called as i unit of measurement or 1 ones. Progressing further, a prepare of such ten "ones" is called as 1 "x". Ahead of tens, a block consisting 10 "tens" is called every bit 1 "hundred" of 100 "ones". For operation on 4-digit numbers, a cake of ten "hundreds" is used as 1 "thousand".
Though base of operations 10 blocks are non very like shooting fish in a barrel to use with the division of big numbers, but they can exist used with numbers up to 100 or g with 2-digit numbers.

Reference image: Base ten blocks to correspond numbers
For example, divide 66 by 5.
- Trade 1 "10" from 6 "tens" with 10 "ones". Now, 6 "tens" and six "ones" are 5 "tens" and xvi "ones".
- Partition the 5 "tens" to 5 individual groups and assign the remaining 16 "ones" to the groups in equal number
- Each "x" has three "ones" and 1 "ones" is left, so the answer/caliber is thirteen and the rest is 1.
- The division equation is 66 ÷ 5 = thirteen and rest ane
Next department reviews the course-wise progression of "sectionalization games".
Progression of Division with Grades
Reference prototype: Course-wise progression of "division"
In grade 3, kids acquire to use the skills of subtraction for agreement the nuts of the division. Also, with the noesis of multiplication of numbers, kids larn to form multiplication tables. With practise, other skills developed at this level are the association of the conceptual knowledge of multiplication and partition to addition and subtraction. Kids also learn about portioning the number of equal size groups. The skill is useful in dividing unmarried-digit numbers by other unmarried-digit using pictures and counters. Other methods of division such every bit "measurement model" (subtracting on a number line) are besides learned.
In grade 4, kids learn to divide numbers ranging from 2-digits to 4-digits with a ane-digit number. Also, division by multiples of 10 and 100 is introduced to apply the skills of representing a number upward to i or two decimal places. Kids as well explore the sectionalisation methodology for calculating a reasonable answer to word problems (quotient) and the rest. Proficiency in mental ciphering and estimation is achieved past the do of using all iv operations on a word problem.
In form v, as kids learn to carve up a number past single-digit number, skills are further honed to split up a number by a 2-digit divisor. Using the noesis of place value system, kids practice dividing a decimal number by a multiple of ten & 100. Also, math skills to perform decimal division by representing a number in fraction form are adult.
Planned math exercises help kids to chief the skills and assimilate the fundamentals of the division.
Learning Methodologies for Division
-
Division, based on subtraction skills
- Sectionalization with pictures – This is the bones and versatile technique to innovate sectionalisation to kids in early grades. Using pictures of objects similar fruits, pencils, or crayons; kids acquire to adapt/separate them in equal size bundles for a stock-still number of groups.
Alternatively, decrease the fixed number of objects from the original gear up (till it becomes empty) to compute the quotient. Kids as well learn to encompass the numbers in suitable terms like dividend, divisor, and caliber to easily frame a mathematical expression on division.
For example – dissever 21 past 7
- Decrease vii from 21 till 0
- = 21 – 7 ➔ 14 – 7 ➔ vii – 7 ➔ 0
- Thus, the caliber is 3 and the remainder is 0
In some other example, dissever 21 past half-dozen
- Subtract 6 from 21 till 0
- = 21 – 6 ➔ 15 – six ➔ 9 – 6 ➔ iii
- Thus, the quotient is 3 and the rest is three
- Framing division judgement – To solve word problems involving division and simultaneously other math operations like add-on (+), subtraction (–) or multiplication (x); students reckon the "sectionalisation" equation with suitable symbols.
- For example, dividing 27 past 9 yields 3.
- Equation: 27 / 9 = iii or 27 ÷ 9 = 3
- Count back to divide – in this partition technique, kids learn to count back on the number line. Mark the "dividend" and number "0" are on the number line to first with. For each jump, every bit illustrated in the effigy, the divisor determines the distance. Subtract it progressively to jump.
- The number of jumps required to reach 0 is the "caliber".
- If no jumps can be fabricated further to reach "0" with divisor, the remaining distance is the "residue".
Using this method, students learn to calculate the remainder in subsequently grades.
Reference paradigm: Divide 24 past iii. Total number of jumps is eight (quotient)
- The relationship betwixt multiplication and sectionalisation – To comprehend division as the contrary of multiplication, 2 equations tin can be used to teach kids about the relationship. An equation with an unknown multiplier and other equation with an unknown divisor are used to notice the unknown quantity. Kids utilize their addition, subtraction besides as multiplication skills (using tables or progressive addition) to notice the unknown value.
- For example: evaluate the unknown quantity in the following equations
- 7 x? = 21
- 21 /? = 7
- To detect the number, kids count the values using a multiplication table or line plots to observe the number of jumps with divisor "vii".
- Work with division equations – To use the math skills of the sectionalization for solving discussion problems and puzzles, division equations are used with the unknown qualifiers. For example, how many kids can equally divide 20 apples within themselves so that each ane of them gets 5 apples?
- The equation will be–
- ➔ 20 ÷? = 5
-
Sectionalisation, using multiplication tables
Learning games on other math skills propel kids to utilise multiplication as progressive addition and utilize the skills in solving puzzles and word bug. With this cognition, kids explicate to form multiplication tables for unmarried-digit numbers and employ these tables for the sectionalization.
For instance, write multiplication table for 6 and eight:
Using multiplication tables, kids can separate a 2-digit number (past the corresponding table) by counting till the residuum is 0.
-
Sectionalisation, based on Number and Operations in base ten
With the knowledge of base of operations 10 blocks, decimal place value system and division equation; kids learn to divide multiples of 10 past similar numbers.
- Division of a multiple of x by some other multiple of 10 – To divide threescore by xx, consider numbers equally bundles of 10s.
- 60 will exist 6 "tens"
- 20 will be 2 "tens"
- The division equation can be written as
- 60 / 20 or
- 6 / 2 in simpler terms to divide rapidly for quotient "3".
- Partitioning of a multiple of 100 by another multiple of 100 – To divide 800 past 400, consider numbers as bundles of 100s
- 800 will be 8 "hundreds"
- 400 volition be 4 "hundreds"
- The division equation can be written as
- 800 / 400 or
- 8 / iv in simpler terms to divide quickly for quotient "ii".
- Division of a multiple of 100 by another multiple of 100 – To divide 700 by 350, consider the numbers as bundles of the same block as "tens" for easy ciphering
- 700 will be vii "hundreds" or 70 "tens"
- 350 will be 35 "tens"
- The division equation tin be written as
- 700 / 350 or
- seventy / 35 (using base 10) for easier division and quotient "ii"
Let's game it:
- Divide by 3
- To divide eighteen by 3, either use multiplication table of 3 or count using sectionalisation model (half-dozen).

- Evaluate
- As 48 / four is 12, 480 can be written as 48 "ones" multiplied by 1 "tens".
- The new equation can be 10 x (48 / 4), so answer is 10 Ten 12. (120)

- Which segmentation sentence will give you the closest judge for the following?
- As the number 3046 is closer to 3200 and 83 is closer to divisor 80, the correct answer can exist selected by interpretation of the nearest numbers.

Application:
"Division" as one of the fundamental math skills is extremely useful in several fields of applied maths (measurement, geometry, trigonometry) and science (chemical sciences, physics and relevant fields of anatomy). "Sectionalisation of numbers" is an essential concept used in geography to rescale the altitude/measurements past segmentation (with the multiples of 10,000 and more) and describe accurate maps. To program a navigational route, such maps are used in marine sciences and other fields.
SplashLearn Division Games Worksheet
Adhering to the common cadre math standards, SplashLearn institutes a well-planned curriculum using interactive worksheets. With the step-by-pace introduction of complex concepts and techniques to primary the associated math skills, kids learn the methods to apply in later on grades without any difficulty. Considering the skill-loss challenges during summertime vacation or to homeschool kids for proficiency in math, comprehensive exercises are instrumental in boosting logical thinking and reasoning.
Source: https://www.splashlearn.com/division-games
0 Response to "How to Pass Level 9 Dividing in 10 Is Again"
Post a Comment